dcmri.AortaKidneys#
- class dcmri.AortaKidneys(organs='comp', heartlung='pfcomp', kidneys='2CF', sequence='SS', **params)[source]#
Joint model for aorta and kidneys signals.
The model represents the kidneys as a two-compartment filtration system and the body as a leaky loop with a heart-lung system and an organ system. The heart-lung system is modelled as a chain compartment and the organs are modelled as a compartment or a two-compartment exchange model. Bolus injection into the system is modelled as a step function.
Injection parameters
weight (float, default=70): Subject weight in kg.
agent (str, default=’gadoterate’): Contrast agent generic name.
dose (float, default=0.2): Injected contrast agent dose in mL per kg bodyweight.
rate (float, default=1): Contrast agent injection rate in mL per sec.
Acquisition parameters
sequence (str, default=’SS’): Signal model.
tmax (float, default=120): Maximum acquisition time in sec.
tacq (float, default=None): Time to acquire a single dynamic in the first scan (sec). If this is not provided, tacq is taken from the difference between the first two data points.
field_strength (float, default=3.0): Magnetic field strength in T.
n0 (float, default=1): Baseline length in nr of scans.
TR (float, default=0.005): Repetition time, or time between excitation pulses, in sec.
FA (float, default=15): Nominal flip angle in degrees.
TC (float, default=0.1): Time to the center of k-space in a saturation-recovery sequence.
Signal parameters
R10a (float, default=1): Precontrast arterial relaxation rate in 1/sec.
S0b (float, default=1): scale factor for the arterial MR signal in the first scan.
R10_lk (float, default=1): Baseline R1 for the left kidney.
S0_lk (float, default=1): Scale factor for the left kidney signal.
R10_rk (float, default=1): Baseline R1 for the right kidney.
S0_rk (float, default=1): Scale factor for the right kidney signal.
Whole body kinetic parameters
organs (str, default=’2cxm’): Kinetic model for the organs.
BAT (float, default=60): Bolus arrival time, i.e. time point where the indicator first arrives in the body.
BAT2 (float, default=1200): Bolus arrival time in the second scan, i.e. time point where the indicator first arrives in the body.
CO (float, default=100): Cardiac output in mL/sec.
Eb (float, default=0.05): fraction of indicator extracted from the vasculature in a single pass.
Thl (float, default=10): Mean transit time through heart and lungs.
Dhl (float, default=0.2): Dispersion through the heart-lung system, with a value in the range [0,1].
To (float, default=20): average time to travel through the organ’s vasculature.
Eo (float, default=0.15): Fraction of indicator entering the organs which is extracted from the blood pool.
Teb (float, default=120): Average time to travel through the organs extravascular space.
Kidney kinetic parameters
kinetics (str, default=’2CFM’). Kidney kinetic model (only one option at this stage).
Hct (float, default=0.45): Hematocrit.
Fp_lk (Plasma flow, mL/sec/cm3): Flow of plasma into the plasma compartment (left kidney).
Tp_lk (Plasma mean transit time, sec): Transit time of the plasma compartment (left kidney).
Ft_lk (Tubular flow, mL/sec/cm3): Flow of fluid into the tubuli (left kidney).
Tt_lk (Tubular mean transit time, sec): Transit time of the tubular compartment (left kidney).
Ta_lk (Arterial delay time, sec): Transit time through the arterial compartment (left kidney).
Fp_rk (Plasma flow, mL/sec/cm3): Flow of plasma into the plasma compartment (right kidney).
Tp_rk (Plasma mean transit time, sec): Transit time of the plasma compartment (right kidney).
Ft_rk (Tubular flow, mL/sec/cm3): Flow of fluid into the tubuli (right kidney).
Tt_rk (Tubular mean transit time, sec): Transit time of the tubular compartment (right kidney).
Ta_rk (Arterial delay time, sec): Transit time through the arterial compartment (right kidney).
Prediction and training parameters
dt (float, default=1): Internal time resolution of the AIF in sec.
dose_tolerance (fload, default=0.1): Stopping criterion for the whole-body model.
free (array-like): list of free parameters. The default depends on the kinetics parameter.
free (array-like): 2-element list with lower and upper free of the free parameters. The default depends on the kinetics parameter.
Additional parameters
vol_lk (float, optional): Kidney volume in cm3 (left kidney).
vol_rk (float, optional): Kidney volume in cm3 (right kidney).
- Parameters:
params (dict, optional) – override defaults for any of the parameters.
See also
Example
Use the model to reconstruct concentrations from experimentally derived signals.
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> import dcmri as dc
Use
fake_tissueto generate synthetic test data from experimentally-derived concentrations:>>> time, aif, roi, gt = dc.fake_tissue() >>> xdata, ydata = (time,time,time), (aif,roi,roi)
Build an aorta-kidney model and parameters to match the conditions of the fake tissue data:
>>> model = dc.AortaKidneys( ... dt = 0.5, ... tmax = 180, ... weight = 70, ... agent = 'gadodiamide', ... dose = 0.2, ... rate = 3, ... field_strength = 3.0, ... t0 = 10, ... TR = 0.005, ... FA = 15, ... )
Train the model on the data:
>>> model.train(xdata, ydata, xtol=1e-3)
Plot the reconstructed signals and concentrations and compare against the experimentally derived data:
>>> model.plot(xdata, ydata)
(
Source code,png,hires.png,pdf)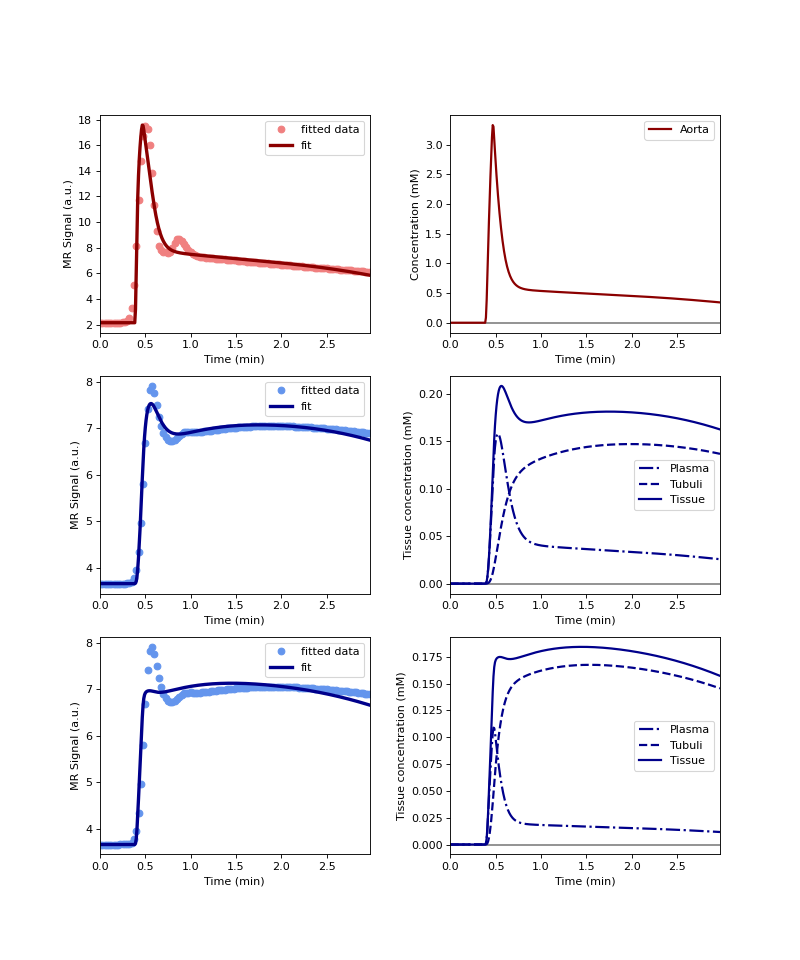
Methods
conc([sum])Concentrations in aorta and kidney.
cost(xdata, ydata[, metric])Return the goodness-of-fit
Return model parameters with their descriptions
load([file, path, filename])Load the saved state of the model
params(*args[, round_to])Return the parameter values
plot(xdata, ydata[, xlim, ref, fname, show])Plot the model fit against data
predict(xdata)Predict the data at given xdata
print_params([round_to])Print the model parameters and their uncertainties
relax()Relaxation rates in aorta and kidney.
save([file, path, filename])Save the current state of the model
set_free([pop])Set the free model parameters.
train(xdata, ydata, **kwargs)Train the free parameters
- conc(sum=True)[source]#
Concentrations in aorta and kidney.
- Parameters:
sum (bool, optional) – If set to true, the kidney concentrations are the sum over all compartments. If set to false, the compartmental concentrations are returned individually. Defaults to True.
- Returns:
time points, aorta blood concentrations, left kidney concentrations, right kidney concentrations.
- Return type:
- cost(xdata: tuple, ydata: tuple, metric='NRMS') float[source]#
Return the goodness-of-fit
- Parameters:
xdata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with time points for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and value.
ydata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with signals for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and values but each has to have the same length as its corresponding array of time points.
metric (str, optional) – Which metric to use - options are: RMS (Root-mean-square); NRMS (Normalized root-mean-square); AIC (Akaike information criterion); cAIC (Corrected Akaike information criterion for small models); BIC (Baysian information criterion). Defaults to ‘NRMS’.
- Returns:
goodness of fit.
- Return type:
- export_params()[source]#
Return model parameters with their descriptions
- Returns:
Dictionary with one item for each model parameter. The key is the parameter symbol (short name), and the value is a 4-element list with [parameter name, value, unit, sdev].
- Return type:
- load(file=None, path=None, filename='Model')#
Load the saved state of the model
- Parameters:
file (str, optional) – complete path of the file. If this is not provided, a file is constructure from path and filename variables. Defaults to None.
path (str, optional) – path to store the state if file is not provided. Thos variable is ignored if file is provided. Defaults to current working directory.
filename (str, optional) – filename to store the state if file is not provided. If no extension is included, the extension ‘.pkl’ is automatically added. This variable is ignored if file is provided. Defaults to ‘Model’.
- Returns:
class instance
- Return type:
- params(*args, round_to=None)#
Return the parameter values
- plot(xdata: tuple, ydata: tuple, xlim=None, ref=None, fname=None, show=True)[source]#
Plot the model fit against data
- Parameters:
xdata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with time points for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and value.
ydata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with signals for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and values but each has to have the same length as its corresponding array of time points.
xlim (array_like, optional) – 2-element array with lower and upper boundaries of the x-axis. Defaults to None.
ref (tuple, optional) – Tuple of optional test data in the form (x,y), where x is an array with x-values and y is an array with y-values. Defaults to None.
fname (path, optional) – Filepath to save the image. If no value is provided, the image is not saved. Defaults to None.
show (bool, optional) – If True, the plot is shown. Defaults to True.
- predict(xdata: tuple) tuple[source]#
Predict the data at given xdata
- Parameters:
xdata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with time points for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and value.
- Returns:
Tuple of 3 arrays with signals for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and value but each has to have the same length as its corresponding array of time points.
- Return type:
- print_params(round_to=None)#
Print the model parameters and their uncertainties
- Parameters:
round_to (int, optional) – Round to how many digits. If this is not provided, the values are not rounded. Defaults to None.
- relax()[source]#
Relaxation rates in aorta and kidney.
- Returns:
time points, aorta relaxation rate, left kidney relaxation rate, right kidney relaxation rate.
- Return type:
- save(file=None, path=None, filename='Model')#
Save the current state of the model
- Parameters:
file (str, optional) – complete path of the file. If this is not provided, a file is constructure from path and filename variables. Defaults to None.
path (str, optional) – path to store the state if file is not provided. Thos variable is ignored if file is provided. Defaults to current working directory.
filename (str, optional) – filename to store the state if file is not provided. If no extension is included, the extension ‘.pkl’ is automatically added. This variable is ignored if file is provided. Defaults to ‘Model’.
- Returns:
class instance
- Return type:
- set_free(pop=None, **kwargs)#
Set the free model parameters.
- Parameters:
pop (str or list) – a single variable or a list of variables to remove from the list of free parameters.
- Raises:
ValueError – if the pop argument contains a parameter that is not in the list of free parameters.
ValueError – If the parameter is not a model parameter, or bounds are not properly formatted.
- train(xdata: tuple, ydata: tuple, **kwargs)[source]#
Train the free parameters
- Parameters:
xdata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with time points for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and value.
ydata (tuple) – Tuple of 3 arrays with signals for aorta, left kidney and right kidney, in that order. The three arrays can all be different in length and values but each has to have the same length as its corresponding array of time points.
kwargs – any keyword parameters accepted by
scipy.optimize.curve_fit.
- Returns:
A reference to the model instance.
- Return type:
Model
